Rigid Flex PCBs — combining flexible and rigid board technologies
A rigid-flex PCB combines rigid PCB sections and flexible PCB sections together into one piece. This allows for optimal configuration to meet the needs of complex and compact electronics designs.
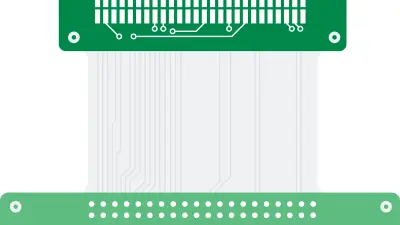
What is a Rigid Flex PCB?
A rigid-flex PCB utilizes a combination of rigid-board and flexible-circuit technology to integrate both rigid and flexible substrates into a single PCB. Rigid sections provide mechanical stability for easy component mounting. Flexible sections allow for dynamic flexing and three-dimensional configuration. Rigid-flex combines the strengths of both into an optimized hybrid solution. This advanced technology offers an optimal blend of flexibility, weight reduction, and durability, making it an ideal choice for modern electronics where space is limited and reliability is critical.
Key features of rigid-flex PCBs:
- Combines rigid and flex PCB segments
- Enables three-dimensional configuration
- Withstands dynamic flexing and bending cycles
- Simplifies complex interconnections
- Fits in products where space is limited
- Allows for movement between the segments of the rigid-flex printed circuit board assembly (PCBA)
- Eliminates connectors and cables

Benefits of Rigid Flex PCBs
Rigid-flex circuit board technology offers many benefits:
Weight reduction
Eliminates external cables and connectors that add weight
Greater spatial efficiency
Conforms to irregular and tight spaces by folding and bending
Reliability
Fewer interconnections mean higher reliability
Cost reduction
Three-dimensional design capability, elimination of connectors, and reduction of total unit size reduces the overall cost of rigid-flex board fabrication
Design freedom
Rigid-flex design enables flexible form factors not possible with rigid PCBs
Manufacturability
Rigid-flex assembly on standard assembly lines for rigid board fabrication
Rigid-Flex PCB configurations
There are several common construction approaches used in rigid-flex PCBs.
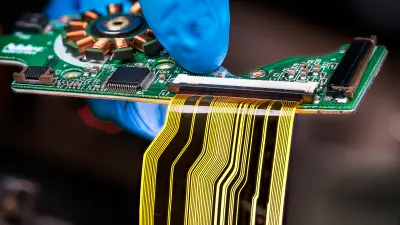
Integrated flex
Rigid and flex sections laminated together into one circuit
Multilayer rigid-flex
Multiple separate rigid layers interconnected by flex layers
Rigid-flex blend
Some layers are continuous while others are discrete or segmented. The optimal choice depends on the complexity, spacing, flexibility, and reliability needs.
Design and manufacturing considerations for Rigid Flex PCBs

Rigid-flex boards involve careful design and fabrication considerations:
- Selection of flexible and rigid base materials
- Dealing with differences in thickness and properties
- Minimizing mechanical stress at transitions
- High precision alignment of layers and flexible components
- Managing the bend radius of flex areas
- Ensuring adhesion and avoiding delamination
- Reliable solder joints on mixed surfaces
Creating a rigid-flex PCB design requires specialized software capable of 3D modeling and other advanced features. Although rigid-flex circuit boards are more costly due to higher material costs and more complex manufacturing, they offer benefits by freeing up additional space, avoiding the use of connectors, and increasing reliability, meaning they outperform standard solutions by far.
With their expertise in flex PCBs as well as rigid boards, copperdot can provide high quality hybrid rigid-flex PCB solutions tailored to your mechanical, electrical, and layout requirements. Contact us to discuss your project needs.
Frequently asked questions about rigid-flex PCBs
Flexible circuit boards excel in applications that require bending and folding. However, rigid-flex PCBs go a step further by offering enhanced mechanical stability and a more extensive range of applications. This is due to the integration of rigid boards that can support heavier components and circuits, thus enabling both dynamic and static applications.
Unlike standard rigid circuit boards, which are mostly confined to static applications, rigid-flex PCBs offer greater design freedom and adaptability. Their flexibility allows them to be fitted into unconventional shapes and sizes, making them perfect for innovative and complex electronic designs.
Rigid-flex boards consist of FR4, polyimide, and adhesiveless liquid crystal polymer (LCP).
FR4 is commonly used in the rigid sections, while polyimide and adhesiveless LCP are options for the flexible layers.
Rigid-flex printed circuit boards allow for extremely high complexity and component density by utilizing flex layers for dense interconnections.
The lifespan of rigid-flex circuit boards largely depends on the conditions in which they operate, a matching layout, and overall design. Properly designed rigid-flex PCBs are generally known for their durability and long service life. That’s why these circuit boards are often used in application with extreme space constraints that demand an enormous degree of reliability, e.g. aerospace or medical applications.
SMD components are bonded with special adhesives. Through-hole plated components can also be mechanically anchored or glued.
Yes, the materials are generally recyclable and comply with RoHS directives.